3
GLOBAL MARKET FOR AGRICULTURAL UNMANNED AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS
The global agricultural drone market is expected to reach a valuation of USD 4.98 billion by 2024 and is projected to continue growing rapidly at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1% from 2024 to 2034, according to consulting firm Fact.MR [20].
Drones are revolutionizing traditional agricultural processes as farmers and agricultural companies aim to maximize production, improve resource consumption, and implement sustainable practices. An increasing number of industry players are recognizing the ability of agricultural drones to provide accurate data collection, efficient monitoring, and high-resolution aerial imagery.
With UAV-based imaging, farmers can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to optimize yield and avoid losses. These drone capabilities include crop monitoring for precision farming and the greening of agriculture. In precision farming systems, the use of agrochemicals is reduced, and significant savings in irrigation water are achieved.
The use of agricultural drones is expected to increase in both developed and developing countries in the near future. The expansion of the agricultural drone market is being driven by governments and organizations recognizing the potential of these technologies and implementing policies and strategies to facilitate their integration into modern agricultural practices.
Data from Bloomberg, based on the MarketsandMarkets™ report, shows that the agricultural drone market was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 17.9 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 31.5%. According to market research from Price-Waterhouse-Coopers, it is forecasted that by 2050, the agricultural UAV market will grow to approximately USD 32.4 billion, accounting for around 25% of the global UAV market [21, 22].
According to Fact.MR research, the global agricultural drone market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 18.64 billion by the end of 2034. It is expected that in 2024, North America will account for 28.7% of the global market.
The East Asian market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 14.1% from 2024 to 2034. The Mexican market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2024 to 2034. By the end of 2034, Japan’s share in the East Asia region is expected to be 24.9%.
This trend is fundamentally transforming the way agricultural producers approach their operations. Within this model, specialized companies offer drone-based services to farmers, providing a range of solutions tailored to their specific needs, including system integration, engineering and consulting, simulation, and training.
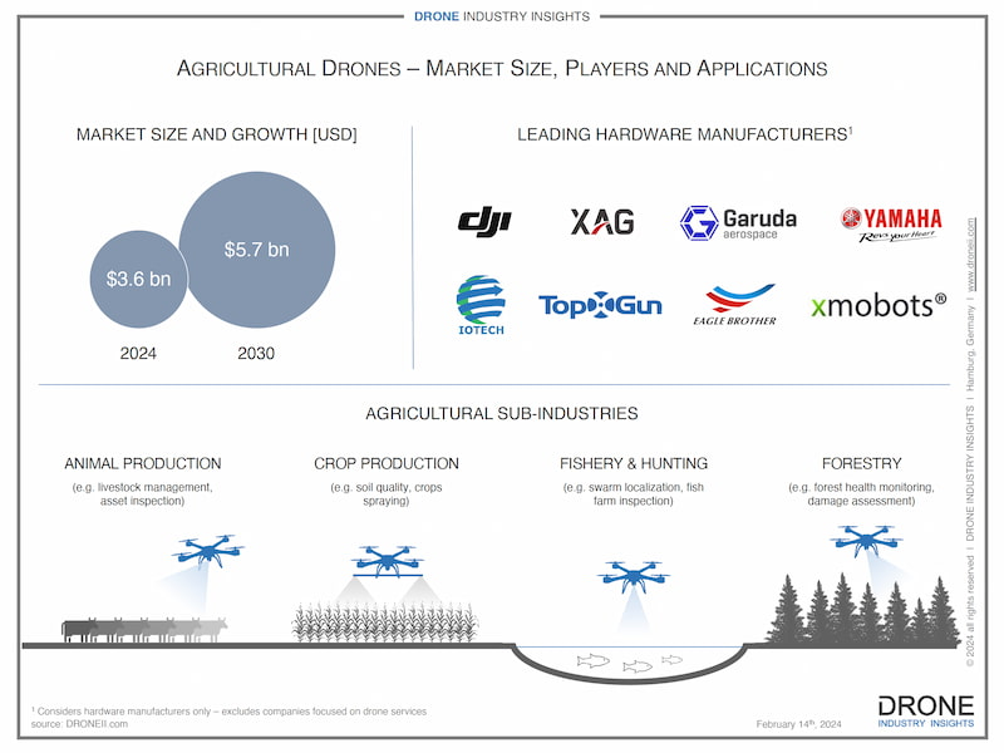
According to Drone Industry Insight, one of the leading global experts in the UAV market, drone-related services already account for 80% of the global drone market. As reported by analysts at Drone Industry Insight (see Fig. 3.2), the agricultural drone market is estimated at USD 3.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 5.7 billion by 2030.
The agency’s analysts categorize agricultural applications to include the use of drones in crop production, livestock farming, fisheries and hunting, as well as in forestry.
According to a report by CCID Consulting, China’s drone market—particularly the sector focused on low-altitude drones such as agricultural UAVs—surged to over USD 68 billion (500 billion yuan) in 2023, representing a robust growth rate of 33.8 percent. Projections indicate that by 2026, this figure could exceed USD 137 billion (1 trillion yuan), underscoring the sector’s rapid expansion and increasing economic significance.
China stands as a dominant force in the global unmanned aerial systems (UAS) market. More than 70,000 companies are currently registered in the country, producing drones and related software. Among commercial UAS applications, mapping and geospatial surveillance currently account for the largest share at 29.3%, while agricultural drones make up approximately 25% [26, 27].
The development of China’s UAS industry has been driven by the formation of high-tech clusters, with Shenzhen leading as the “drone capital.” This region is marked by a strong innovation support framework, including favorable legal regulations for mini and lightweight drones, direct investment programs, and risk mitigation initiatives for startups. These initiatives generate up to 200 new industry projects annually. Furthermore, the cluster system facilitates direct cooperation between enterprises and research institutions, while also providing streamlined access to suppliers and resources.
By leveraging the clustering effect—similar to Silicon Valley in the early 1990s—China has built up the capacity, expertise, and logistical infrastructure necessary to maintain a strong competitive advantage on the global stage [28].
The aggressive growth of China’s UAS industry is further fueled by political and regulatory support, along with significant investment from the government. According to the latest UAS development guidelines released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), the ministry plans to establish and revise over 200 regulations covering the research, manufacturing, application, and safety oversight of civil drones. In addition, in May 2021, Chengdu Aircraft Industry Group (CAIG)—a subsidiary of the state-owned Aviation Industry Corporation of China—signed an agreement with the Sichuan provincial government to jointly invest approximately USD 1.55 billion in building an industrial park dedicated to UAS development [29].
China’s drone industry is notably led by Da-Jiang Innovations (DJI), a company that sets the pace for the global unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) sector. DJI manufactures over 70% of the world’s commercial drones. In 2021, the company produced approximately 135,000 agricultural drones, and by 2022, that number had increased to over 200,000 units [29, 30, 26]. According to experts, DJI’s competitive advantage lies in its integration across the entire value chain—from sourcing raw materials to production, innovation, and logistics. Another key factor is the relatively low cost of hardware and software development, manufacturing, and supply chains, all of which reflect the broader characteristics of the Chinese economy.
The high level of domestic drone production has driven widespread adoption and affordability for Chinese consumers. Private sector players are actively developing hardware, platforms, analytics, training, and service solutions. Public support for the industry includes a variety of local and national subsidy schemes and incentives aimed at promoting advanced technologies and modernization, as well as encouraging the purchase of drones and related services.
At the current stage, agricultural drones in China primarily perform two core functions: visualization and analytics, and crop spraying. Companies focusing on agricultural drone-based visualization include SenseFly and Beijing-based developers. Prominent manufacturers of crop protection drones include several domestic brands such as XAG (formerly XAircraft), DJI, Gaoke Xinnong (GKXN), Guangzhou TXA Aviation, Beidahuang Agriculture Aviation, AnYang Quanfeng Aviation, Xinjiang Tianshayuren, Shenzhen Hi Tech New Agriculture, and Wuxi Hanhe Aviation.
China’s agricultural UAV market is experiencing a rapid boom, supported by strong government policies. Agricultural drones have been included in the national subsidy list for essential farming equipment. Even drone rentals are eligible for subsidies, leading to a rise in service providers offering drone-based crop spraying and fertilizer application. For so-called “smart” agricultural machinery, inclusion in the state subsidy program has become a major driver of growth [32].
The active development of agricultural drone applications in North America is primarily based on the advanced scientific and technological potential of the United States. Experts also attribute this progress to the vast expanses of arable land, where the deployment of agricultural drones can significantly increase operational efficiency, improve productivity, and reduce resource consumption. Another major factor driving demand for agricultural drones is the widespread adoption of precision agriculture systems, which are particularly prevalent on this continent. Until recently, North America had been the largest and most advanced market for the implementation of innovative agricultural technologies (note: China has now taken the lead in agricultural drone deployment).
Government initiatives have played a decisive role in promoting drone usage in U.S. agriculture. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) offer grants and funding opportunities to support the adoption of drones in farming practices. This support encourages innovation, facilitates farmers’ access to necessary resources, and promotes the seamless integration of UAVs into agricultural operations. Integration with farm management systems has enhanced the overall efficiency of drone applications. Even small family-owned farms—which account for 90% of all farms in the United States—utilize drones by contracting with service providers for aerial imaging and crop spraying with fertilizers and pesticides. UAVs also help mitigate the labor shortage, especially considering the average age of an American farmer is 57.5 years. According to a study by the American Farm Bureau Federation, U.S. farmers using agricultural drones see a return on investment of approximately $12 per acre for corn and $2 to $3 per acre for soybeans and wheat [33].
Europe represents one of the most advanced markets for the adoption of innovative technologies in agriculture, which contributes to steady market growth across the region. Geographically, the European agricultural drone market encompasses Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, and other European nations. Germany holds a dominant share of this market due to its targeted digitalization policies in the agricultural sector, including increasing government initiatives aimed at agrarian development. As early as 2019, the German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) launched the “Digital Experimental Fields” initiative to support the digital transformation of German agriculture. In addition, 14 distinct research projects addressing key agricultural topics have been initiated in various regions across the country. Currently, one in ten farmers in Germany uses drones. Germany is also actively engaged in international cooperation, including joint ventures with China. For instance, German industrial giants such as Bosch and Continental AG are collaborating with the Chinese company Baidu Bosh on AI-based autonomous vehicle systems.
The European agricultural drone market is expanding rapidly and is expected to continue growing due to favorable regulations, technological advancements, a strong agricultural sector, and an emphasis on sustainable farming practices and precision agriculture. Experts believe that Europe also has the advantage of developing a unified legal framework across its member states. Transparent regulations and government incentives have been implemented to ensure the safe and widespread use of drones in agriculture. In 2021, the European Union introduced initiatives such as the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) and the European Innovation Partnership for Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability to support innovation in the sector. Europe’s well-established agricultural sector and the increasing demand for efficient farming methods are driving the adoption of agricultural drones. The region also hosts leading drone manufacturers, a robust ecosystem of research institutions, and strong industry collaboration, all of which foster innovation and the exchange of knowledge in this field [34].
The global agricultural drone manufacturing market is undergoing rapid transformation. The industry is in a phase of sustained long-term growth, which allows previously lesser-known players to enter the ranks of industry leaders through quicker innovation adoption, cost reductions, and faster time-to-market strategies.
The key players in the agricultural drone market with advanced innovation capabilities include DJI (China), XAG (China), Garuda Aerospace (India), IO TechWorld (India), TopXGun (China), Eagle Brother (China), and Xmobots (Brazil) [35].
In conclusion to this section on the international market and its developments, it is important to note the following: the integration of drones into global agriculture has occurred gradually. This is partly due to the inherent conservatism of traditional farming practices, which are often passed down through generations. However, it also results from regulatory restrictions in various countries. As a result, by 2024, stark differences have emerged between countries with similar agricultural needs but varying regulatory environments. While the laws of physics and biology remain constant across borders, legislation has become a decisive factor—either accelerating technological advancement in agriculture or relegating heavily regulated countries to the back of the line in terms of progress.
Overall, despite certain challenges, the outlook for the agricultural drone market remains positive as of 2024. The sector is on a growth trajectory and holds significant potential for future expansion. This growth is supported by increasing awareness of the unique benefits drones offer in agriculture. As regulatory frameworks and technologies continue to evolve, drones are poised to play an increasingly important role in enhancing efficiency and productivity in the agricultural sector.